Product Description
While many airplane hangar manufacturers offer one or two designs with stock options, we can help you customize your hangar design just how you want it. Your new steel hangar kit can be designed to accommodate any type of aircraft, thanks to our wide range of door options, as well as adapted to incorporate living quarters or be built as a part of another building type – even an entire metal home.
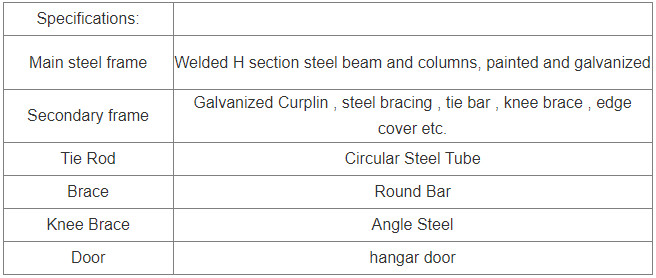

About Steel Structure Aircraft Hangar
Steel structure aircraft hangars are specialized buildings designed to house and protect aircraft. They are constructed primarily using steel due to its strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some key aspects of steel structure aircraft hangars:
Design and Construction: Aircraft hangars are typically large, open structures with high ceilings to accommodate various sizes of aircraft. The steel frame provides the structural support needed to span wide distances without the need for internal columns, allowing for unobstructed movement of aircraft.
Roofing: The roofing of steel structure aircraft hangars is often made of steel panels or other durable materials. The roof is designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and provide adequate protection for the aircraft stored inside.
Doors: Aircraft hangars are equipped with large doors, such as sliding doors or bi-fold doors, to allow aircraft to enter and exit the hangar easily. These doors are often designed to be weatherproof and secure.
Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential in aircraft hangars to ensure proper air circulation and prevent the buildup of fumes and gases from aircraft engines. Ventilation systems are designed to provide fresh air while maintaining the hangar's structural integrity.
Lighting: Aircraft hangars require ample lighting to allow for safe movement of aircraft and personnel. Hangars are equipped with high-intensity discharge (HID) or LED lighting systems that provide bright, uniform illumination throughout the hangar.
Size and Configuration: Steel structure aircraft hangars can vary in size and configuration depending on the number and size of aircraft they are designed to accommodate. They can range from small, single-aircraft hangars to large, multi-bay hangars capable of housing multiple aircraft simultaneously.
Applications: Steel structure aircraft hangars are used by commercial airlines, private aircraft owners, and military organizations to store and maintain aircraft. They are also used for aircraft manufacturing and maintenance operations.
Function
Site Selection: Choose a site that is large enough to accommodate the hangar and allows for future expansion if necessary. Consider factors such as accessibility for aircraft, proximity to runways, and local regulations regarding land use.
Foundation: The type of foundation will depend on factors such as soil conditions, local building codes, and the size of the hangar. Common foundation types include concrete slab, pier and beam, and deep foundations like piles or caissons for areas with poor soil stability.
Steel Framing: Steel framing offers strength, durability, and flexibility in design. Consider the type of steel to be used (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel) and the framing system (e.g., rigid frame, arch frame) based on the hangar's size and structural requirements.
Roofing and Cladding: Choose roofing and cladding materials that provide weather protection, insulation, and aesthetic appeal. Options include metal panels, standing seam roofs, insulated panels, and translucent panels for natural lighting.
Doors: Hangar doors must be large enough to accommodate the aircraft and should operate smoothly and efficiently. Options include bi-fold doors, sliding doors, and hydraulic doors, each with its own advantages and considerations regarding clearance and opening mechanisms.
Utilities: Plan for utilities such as electricity, water, sewerage, and telecommunications to support hangar operations. Consider the location of utility connections, distribution systems, and any special requirements for aircraft maintenance equipment.
Environmental Considerations: Implement sustainable design practices and environmental mitigation measures where possible. This may include energy-efficient lighting, rainwater harvesting systems, and landscaping to reduce heat island effects.
Safety and Security: Prioritize safety measures such as emergency exits, fire extinguishing systems, and clear signage. Install security features such as perimeter fencing, access control systems, CCTV cameras, and intrusion detection sensors to protect the hangar and its occupants.
Accessibility: Ensure the hangar is accessible to personnel, vehicles, and equipment. Provide adequate parking areas, loading docks, and maneuvering space for vehicles and aircraft.
Maintenance and Operations: Develop a maintenance plan for the hangar structure and its components, including regular inspections, repairs, and upgrades as needed. Consider operational requirements such as lighting controls, HVAC maintenance, and waste management.